The Stigma of COVID-19 And Its Influence on The Management of COVID-19 Stigma of COVID-19
Abstract
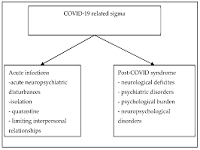
Background: Negative stigma related to COVID-19, which has a social impact, among others, can cause an individual to hide their illness to avoid discrimination, prevent people from seeking immediate health care when experiencing symptoms, prevent individuals from developing healthy behaviors, and contribute to more severe health problems, ongoing transmission, and difficulties in controlling the spread of the COVID-19 virus.
Objectives: The purpose and aim of conducting this research are to determine the effect of the stigma of COVID-19 on health care for individuals infected with COVID-19.
Materials and methods: This research is descriptive research with quantitative and qualitative methods as a complement. Respondents involved in the quantitative method were 291 people, and qualitative (in-depth interviews) were 21 key informants. The research was carried out in 4 cities in Indonesia from December 2022 to June 2023.
Results: Most were women (69.8%), aged 26-35 years (37.1%), Diploma/Undergraduate (66.7%), and worked as government employees (28.9%). This research found that 59.1% of respondents have moderate knowledge about COVID-19, and 83.8% answered that they really need information related to COVID-19. Regarding trust in information sources, most respondents (83.8%) responded that they trust it. We also found that 79.4% of the respondents has moderate behavior towards the pandemic, and 74.6% have average emotional well-being. Stigma was evaluated through questionnaires distributed in a guided manner with the result that 6.19% of the 291 respondents experienced stigma, while 93.8% had no stigma related to COVID-19. Multiple linear regression tests found that the significance value for the influence of knowledge, the need for information, trust in information sources, behavior towards pandemics, and emotional well-being simultaneously for stigma is 0.000 < 0.05. The calculated F value is 4.716 > F table 2.25, so it can be concluded that the above factors significantly influence simultaneous Stigma.
Conclusion: This study found that knowledge, need for information, trust in information sources, attitudes towards pandemics, and emotional well-being simultaneously have a significant effect on Stigma.